Hello,大家好!今天我们来聊聊Meta最新发布的Llama 3.1系列模型中的新功能 —— 工具调用能力。这个功能不仅仅是Llama3.1独有,最近发布的Mistral NeMo和Mistral Lager2也都已经支持了工具调用能力。我觉得其本质还是为了减少LLM的”幻觉“现象。
定义
Llama3.1工具调用
简单来说,工具调用允许大语言模型(LLM)在对话过程中直接使用预定义的工具,就像我们使用各种App一样。这大大扩展了AI的能力范围,使它能够更好地解决实际问题。
- Llama 3.1内置了三种特定工具:Brave Search、Wolfram Alpha和Code Interpreter。
- 这些工具直接集成在模型中,很重要一点,搜索引擎的API还是需要的。
- 工具调用是模型训练的一部分,模型知道如何和何时使用这些工具。
Llama 3.1的内置工具
Llama 3.1内置了三种强大的工具:
- Brave Search: 用于网络搜索,让AI能获取最新信息,这里指的网络搜索并不是直接在网上搜索信息,而是需要通过搜索引擎的API接口才能进行网络搜索。
- Wolfram Alpha: 用于复杂数学计算,提升AI的数学能力。
- Code Interpreter: 允许AI直接输出和执行Python代码。
这些工具使Llama 3.1能够执行从信息查询到数学计算,再到编程任务的广泛操作。
Llama 3.1的工具调用的工作原理
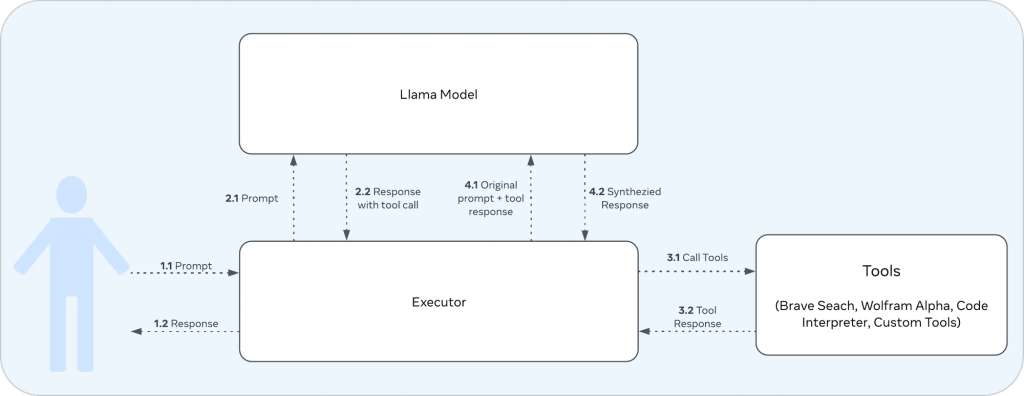
工具调用的工作流程大致如下:
- 用户交互:
- 1.1: 用户向执行器(Executor)发送提示(Prompt)。
- 1.2: 执行器最终将响应(Response)返回给用户。
- 执行器与Llama模型的交互:
- 2.1: 执行器将用户的提示传递给Llama模型。
- 2.2: Llama模型生成包含工具调用的响应。
- 执行器与工具的交互:
- 3.1: 执行器根据Llama模型的响应调用相应的工具。
- 3.2: 工具执行后返回结果给执行器。
- 执行器再次与Llama模型交互:
- 4.1: 执行器将原始提示和工具调用结果一起发送给Llama模型。
- 4.2: Llama模型生成最终的综合响应。
这张图就是一个完整的工具调用循环,从用户输入到最终输出,包括了Llama3.1模型的决策过程、工具的调用,以及如何将工具的结果整合到最终响应中。这种设计允许Llama3.1模型利用其内置的工具来增强能力,能够快速、精准地回答用户的问题,减少”幻觉“现象。
举一个例子:
我们先拟人化三个角色,你(用户),你的天才朋友(Llama3.1),你的小助手(Executor)
- 你问一个问题,比如:今朝上海天气哪能讲?
- 小助手把问题转交给你的天才朋友,你的小助手说:有则赤佬问上海天气情况。
- 天才朋友思考后决定需要查看天气预报,他说:阿拉得查查天气预报App。
- 小助手去查天气预报App(这就是调用工具)打开APP查上海天气。
- 小助手把上海天气信息告诉天才朋友,他说:今朝上海天气哈捏有36度,伐落雨。
- 天才朋友结合这条信息给出完整回答”根据天气预报App,今天上海是个晴朗得好天气,温度36度,适合待在家里吹空调。“
- 小助手把这个回答告诉你(用户)。
所以,通过这种方式,大语言模型给到用户得回答即高效又精准。
参数说明
我们结合Meta的官方文档(建议刚开始玩llama系列模型的小伙伴还是先去看一下原文档),提取一些比较重要的内容和参数拎出来讲一讲。
这次的提示词格式有所变动,尤其是角色方面分别是:
system :设置与 AI 模型交互的上下文。它通常包括帮助模型有效响应的规则、准则或必要信息。
user :表示与模型交互的人类。它包括模型的输入、命令和问题。
ipython :Llama 3.1 中引入的新角色。从语义上讲,这个角色的意思是“工具”。此角色用于在从执行器发送回模型时,使用工具调用的输出标记消息。
assistant : 表示 AI 模型根据 ‘system’、’ipython’ 和 ‘user’ 提示中提供的上下文生成的响应。
Python示例如下:
<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
Environment: ipython
Tools: brave_search, wolfram_alpha
Cutting Knowledge Date: December 2023
Today Date: 23 Jul 2024
You are a helpful assistant<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
What is the current weather in Menlo Park, California?<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>Environment这里的环境定义为:
- ipython:我理解就是代码解释器
Tools这里的工具定义为:
- brave_search:网络搜索
- wolfram_alpha:数学计算器
示例说明
我们用下面这段脚本来试试最新的Llama3.1的网络搜索能力,以下是一些前置条件:
- 安装Python语言
- Ollama框架已安装;
- Llama3.1系列模型已下载;
- Python的requests库已安装;
- 搜索引擎的API已开通;
推荐:Google、Bing、DuckDuckGo,Brave相关链接都在文尾
以下示例在Windows环境下运行:
import json
import requests
import re
# Bing API 设置
subscription_key = "BING API KEY" # 请替换为您的实际 Bing API 密钥
endpoint = "https://api.bing.microsoft.com/v7.0/search"
def call_ollama(prompt, system_prompt):
url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"
data = {
"model": "llama3.1:8b",
"prompt": prompt,
"system": system_prompt,
"stream": False
}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
return response.json()['response']
def brave_search(query):
headers = {"Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key": subscription_key}
params = {"q": query, "textDecorations": True, "textFormat": "HTML"}
try:
response = requests.get(endpoint, headers=headers, params=params)
response.raise_for_status()
search_results = response.json()
if "webPages" in search_results and "value" in search_results["webPages"]:
results = []
for item in search_results["webPages"]["value"][:3]:
results.append(f"Title: {item['name']}\nURL: {item['url']}\nSnippet: {item['snippet']}\n")
return "\n".join(results)
else:
return "No results found."
except Exception as ex:
return f"Error during search: {str(ex)}"
def process_model_output(response):
match = re.search(r'<function=brave_search>\s*({.*?})\s*</function>', response)
if match:
return match.group(1)
match = re.search(r'(?:<\|python_tag\|>)?function=brave_search>\s*({.*?})\s*(?:<\|eom_id\|>)?', response)
if match:
return match.group(1)
return None
def main():
system_prompt = """
Environment: ipython
Tools: brave_search
# 工具使用说明
- 当需要搜索信息时,务必使用 brave_search 函数。
- 必须使用这个精确格式进行搜索:<function=brave_search>{"query": "你的搜索查询"}</function>
- 不要使用 <|python_tag|> 或其他标签。
- 在收到搜索结果后,总结找到的信息。
- 只使用搜索结果中的信息,不要使用预先存在的知识。
你是一个能够搜索实时信息的有用助手。请始终用中文回答用户的问题。
"""
print("Welcome to the Llama 3.1:8b assistant with web search integration!")
print("Type 'quit' to end the conversation.")
while True:
user_prompt = input("\nPlease enter your question: ")
if user_prompt.lower() == 'quit':
print("Thank you for using the assistant. Goodbye!")
break
response = call_ollama(user_prompt, system_prompt)
print("\nLlama 3.1:8b:", response)
search_query_json = process_model_output(response)
if search_query_json:
try:
search_query = json.loads(search_query_json).get("query", "")
if search_query:
print(f"\nPerforming web search for: {search_query}")
search_result = brave_search(search_query)
print("Search results:", search_result)
follow_up_prompt = f"Based on the search results: '{search_result}', please provide a brief summary or answer to the original question: '{user_prompt}'"
follow_up_response = call_ollama(follow_up_prompt, system_prompt)
print("\nLlama 3.1:8b:", follow_up_response)
else:
print("Search query is empty.")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"Error parsing JSON: {search_query_json}")
else:
print("No valid search function call detected.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()1. 导入必要的库:
import json
import requests
import rejson: 用于处理JSON数据requests: 用于发送HTTP请求re: 用于正则表达式操作
2. Bing API 设置:这里不一定要使用bing,各大搜索引擎都可以,只要是开放API的
# Bing API 设置
subscription_key = "BING API KEY" # 请替换为您的实际 Bing API 密钥
endpoint = "https://api.bing.microsoft.com/v7.0/search"这里设置了Bing搜索API的密钥和接口地址。
3. call_ollama 函数:
def call_ollama(prompt, system_prompt):
# ...这个函数用于调用Llama 3.1模型。它向本地运行的Ollama服务发送请求,获取AI的回应。
4. brave_search 函数:
def brave_search(query):
# ...这个函数实际上使用Bing API进行搜索。它发送搜索请求并处理结果,返回前三个搜索结果的摘要。
5. process_model_output 函数:
def process_model_output(response):
# ...这个函数用正则表达式从AI的回应中提取搜索查询,它能处理不同格式的函数调用,经过验证效果并不好,同时我也没太多时间在这里做优化,有兴趣的小伙伴可以尝试不同函数。
6. main 函数:
def main():
# ...7. 系统提示:
system_prompt = """
# ...
"""这里的system_prompt还是蛮重要的,在使用8B尺寸的模型时尽量简单些,70B以上可以复杂一些。
8. 主循环:
- 接受用户输入
- 调用AI获取回应
- 如果AI要搜索,就执行搜索
- 将搜索结果给AI,获取最终回答
9. 脚本入口:
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()使用示例
1. 首先,我们得创建一个空的文件夹,在该文件夹内创建一个空的文件,把以上这段代码复制到一个空的文件里,txt文件也是可以的,但是文件保存要把文件格式改成*.py;

2. 接着,我们在该文件夹下“右击”再“点击”在终端中打开;
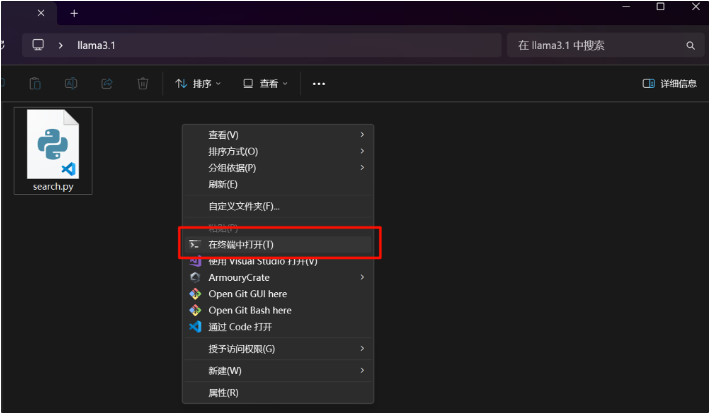
3. 在保证前置条件都已安装完成的情况下,输入 python search.py 这条命令开始执行该脚本;
4. 输入问题,比如:请总结下kunpuai.com这个网站;
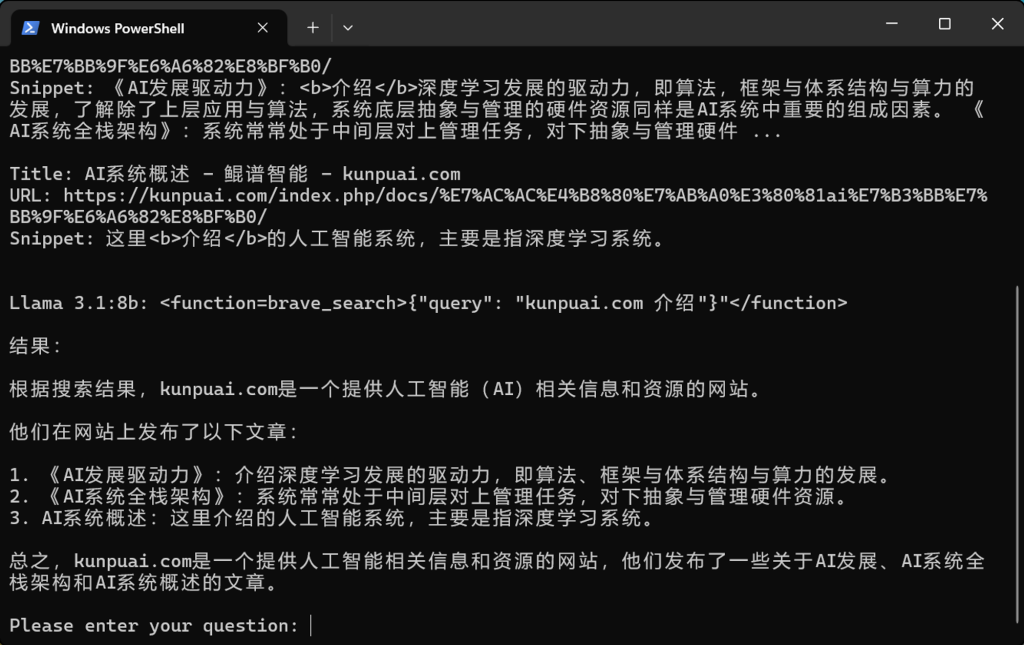
5. 这是Llama3.1 8B总结的效果,由于在brave_search 变量里设置了3,所以会有3条结果。
好了,以上便是这次网络搜索工具的示例,8b的模型推理非常流畅,但是推理结果却显得很一般,可以尝试更大尺寸的模型。欢迎小伙伴尝试,不过讲老实话,Bing的搜索引擎API开通还是比较麻烦的。有经验的小伙伴我们可以交流交流,有没有更好的办法。
Google搜索引擎:https://serpapi.com/
duckduckgo搜索引擎:https://duckduckgo.com/
Bing搜索引擎:https://azure.microsoft.com/services/cognitive-services/bing-web-search-api/
Brave搜索引擎:https://api.search.brave.com/
Meta文档:https://llama.meta.com/docs/model-cards-and-prompt-formats/llama3_1